Setting up an Ingress in Rancher
In kubernetes, Services are only internally available. To expose these to the internet, we use an Ingress resource.
Ingress Configuration
1. Choosing a domain
For acceptance, test and staging enrivonments, you can optionally use DNS suffixes which are automatically routed to the environment. Examples can be:
*.pleaseaskm.harborn.dev, use this for dev environments.*.pleaseaskm.com, use this for production environments.
For example, if setting up an environment with a backend and frontend should be done like this:
my-app.pleaseaskm.com(frontend)my-app-backend.pleaseaskm.com(backend)
2. Setting up the containers
Navigate to Ingresses via Service Discovery -> Ingresses. To set up your ingress correctly, set the following attributes:
Namespace: Select the desired namespace.Name:project-name.-
Rules:- Request Host: The domain chosed in the previous step.
- Path: Select
Prefix. If you want all traffic on that domain to go to the container (in most cases) the the path to/. If you want to limit the traffic to a specific path, set that path (e.g/api,/admin, etc...) - Target Service: Select the container (e.g
my-application) - Port: Select the correct port for your container (e.g.
3000,80,8080)
-
Using the left menu, select
Ingress classand usenginx.
3. Creating a certificate
To setup a certificate, traffic should already be directed to the hosting environment. If this is not the case, please set up your DNS records correctly.
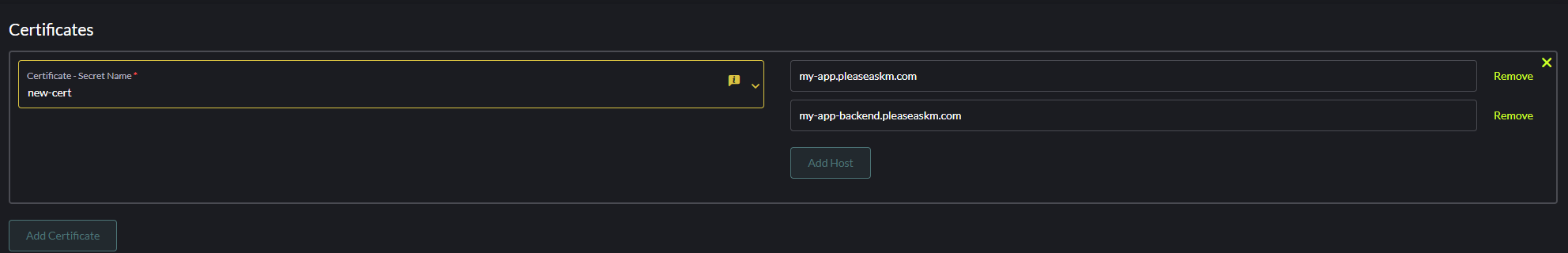
Firstly, we're going to create the certificate in the ingress. Click edit on your ingress and navigate to Certificates. Please note, certificate names should be unique. If setting up multiple certificates for a single project, make sure the certificates have a different name. Click Add certificate and manually type the name of the certificate you want to create. When typing, a dropdown is shown and you should manually click (do not use enter on your keyboard) the name. If done correctly, you should see an orange outline around the certificate name. This is because Rancher will create the secret for us when validating the certificate. Now, add all domains for this certificate in the same tab. Use the Add host button to add a host for this certificate. Note, if a single host fails, the entire certificate will fail.
Lastly, we need to setup annotations which allows Rancher to validate the hosts and grant us the certificate. We do this by adding a single annotation:
Annotations:- Key:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer. - Value:
letsencrypt.
- Key:
4. Altering NGINX behaviour
All ingresses are managed by NGINX. When creating an ingress, a nginx configuration snippet is sent to the nginx controller to direct traffic to your container. We can use annotations to alter the snippet being sent to the nginx controller. Please only use these when a change is required. A complete list of annotations can be found here: Ingress NGINX annotations
Here is a list of some common ones used:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 32m, increases the upload size limit.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: 100k, increases the header limit which can be used if hitting header size limits (e.g. Symfony debug headers).